
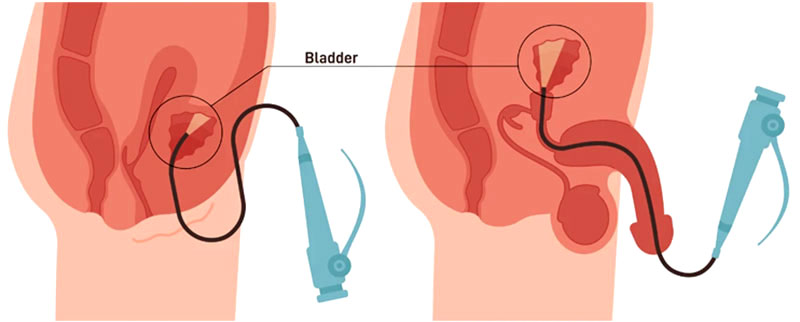
Diagnostic cystourethroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used primarily in urology to inspect the interior of the bladder and urethra. Utilizing a cystoscope equipped with a camera and light source, the procedure provides a direct visual assessment to detect abnormalities such as tumors, strictures, or infections. It also offers the opportunity to perform interventions like biopsies or minor therapeutic measures during the same session. This procedure plays a critical role in both the diagnostic and treatment pathways for various urinary tract conditions.
Treatment
While diagnostic cystourethroscopy is primarily an evaluative tool, it often transitions into a treatment modality when abnormalities are detected. Key treatment aspects include:
- Biopsy and Tissue Sampling: During the examination, small tissue samples can be collected for histopathological analysis. This helps in confirming diagnoses such as cancer, inflammation, or infection.
- Therapeutic Interventions: In some cases, minor treatments can be performed simultaneously. For example, laser ablation of small lesions, fulguration of bleeding points, or dilation of strictures may be undertaken to relieve symptoms and improve urinary function.
- Post-Procedure Care: Following the intervention, patients may receive antibiotics to prevent infection and be advised on lifestyle modifications or follow-up procedures to monitor treatment effectiveness.
Surgical Approach
When the need for intervention escalates beyond minor treatments, a surgical approach may be considered. Although cystourethroscopy is minimally invasive, certain conditions require more extensive surgical management:
- Endoscopic Surgery: Many urological procedures now use endoscopic techniques, where cystourethroscopy acts as both a diagnostic and therapeutic tool. For example, endoscopic resection of bladder tumors is a common surgical intervention.
- Advanced Instrumentation: Modern cystoscopes are designed with channels for surgical instruments, enabling procedures such as stone removal or tumor resection without the need for open surgery. This reduces recovery time and minimizes complications.
Prevision
Proper preoperative planning is essential to ensure the safety and success of cystourethroscopy and its associated interventions. Key prevision measures include:
- Preoperative Testing: Routine blood tests, urine analysis, and imaging studies (such as ultrasound or CT scans) are performed to gain a full picture of the urinary tract’s anatomy and to plan the procedure accurately.
- Informed Consent: Clear communication regarding the procedure’s purpose, potential risks, benefits, and possible complications is essential. Patients should be fully informed and consent obtained prior to the procedure.
- Patient Preparation: Preoperative instructions may include fasting guidelines or adjustments to current medications. Additionally, patients are advised on post-procedure care to ensure a smooth recovery.
Diagnostic cystourethroscopy is a pivotal procedure in modern urology that not only enables direct visualization of the bladder and urethra but also facilitates early detection of abnormalities ranging from infections to malignancies.