
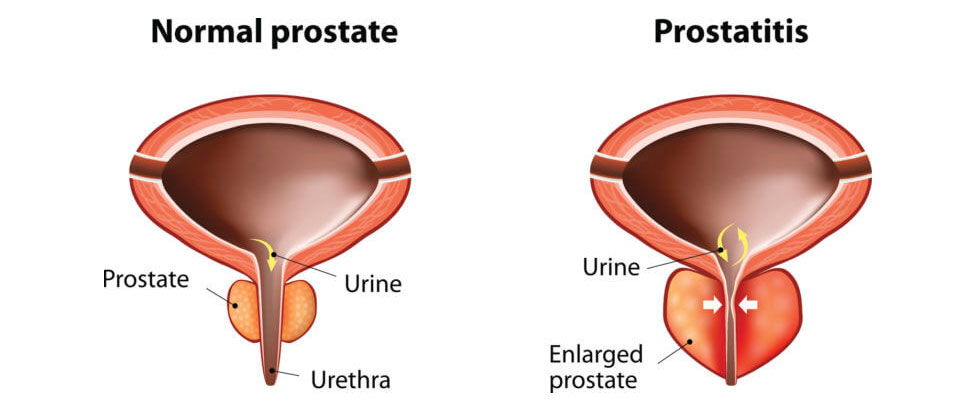
Medical and surgical management of prostate enlargement, also known as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), depends on the severity of symptoms and the impact on a patient’s quality of life. Medical treatment is usually the first line of management and includes medications like alpha-blockers (e.g., tamsulosin, alfuzosin) that relax the muscles of the prostate and bladder neck to improve urine flow, and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors (e.g., finasteride, dutasteride) that shrink the prostate over time. In some cases, combination therapy is used for better symptom control. Lifestyle changes such as reducing fluid intake at night, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and bladder training can also help manage mild symptoms.
When medications are ineffective or symptoms are severe—such as urinary retention, recurrent infections, bladder stones, or kidney damage—surgical intervention is recommended. The most common surgical procedure is Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP), where excess prostate tissue is removed using an instrument inserted through the urethra. Newer minimally invasive techniques like laser enucleation, UroLift, and Rezum therapy offer effective alternatives with quicker recovery times and fewer complications. Surgical treatment provides long-term relief of symptoms and significantly improves urinary function and quality of life.